There are a number of ways to white balance footage in After Effects and Premiere Pro, and Chris and Trish Meyer recently added another method, sampling with the Tint effect on a Solid layer set to Divide mode above the source layer. Eran Stern also recently added a method, using CC Color Neutralizer in Premiere.
The same class has more great explanations of using solids and gradients for tinting, as well as a Modes explained module. There's older similar pieces on PVC, Blend Modes in Adobe Premiere Pro and CMG Hidden Gems: Chapter 9 – Blending Modes, but the movies on modes really do explain the composite modes and blending mode groups well. You can dig deeper on the newer modes with Ben Rollason (AE scripts), who showed how to emulate these modes before they appeared in After Effects in Subtract and Divide Blending Modes in AE CS4.
There isn't a one-click solution for white balance by Adobe, but a simple tool had been offered by Francois Tarlier, ft-Auto White Balance, which wasn't upgraded past CS6. If the Divide mode solid method isn't for you, it may or may not take only a few more clicks with the more established methods offered by Adobe. In color correction, tonal correction generally comes first: black levels first, then white levels. There's much more on color correction in general in Premiere Pro Help.
For all things color, see the Tao of Color Grading newletter for regular news on color correction and grading. You can find comprehensive authoritative information on color correction from Alexis Van Hurkman in his Color Correction Handbook: Professional Techniques for Video and Cinema. Peachpit Press has a sample chapter on Primary Color Adjustments, if you want a peek. Also quite good are books from Steve Hullfish: Color Correction for Video (older but practical) and The Art and Technique of Digital Color Correction (practical plus drawing from top colorists).
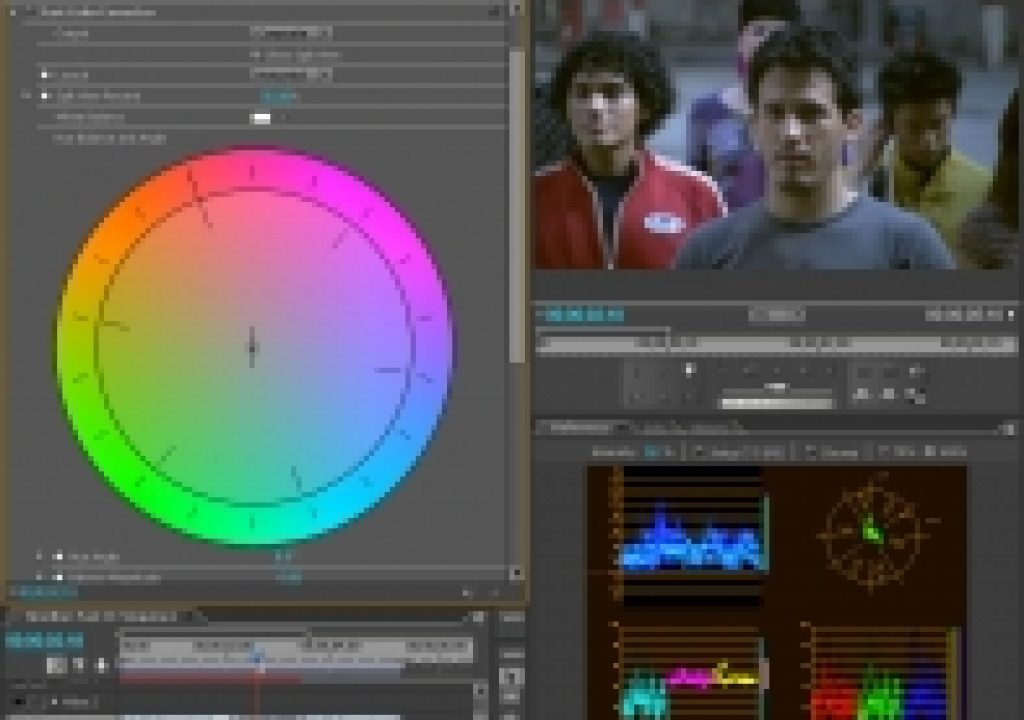
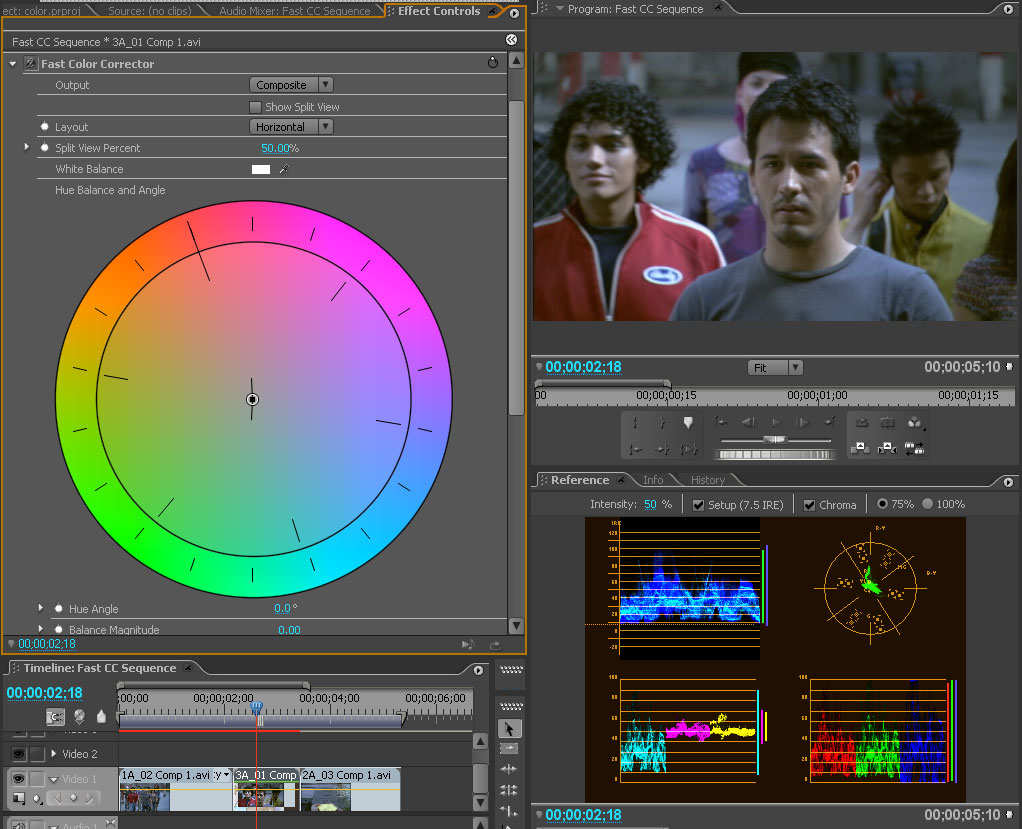
Andrew Devis explains using the the White Balance control chip in the Fast Color Corrector in Premiere Pro CS6 Techniques: 51 Color FIVE: Color Cast (Fast Color Corrector does dynamic link to AE, but without the pretty UI). If you're looking for a more succinct explanation see Pamela Berry's video tip. You'd still most likely need to adjust black and white levels, since White Balance changes color wheel balance and gain but doesn't isolate luminance.
By the way, there's also an Auto Balance control in Red Giant Colorista II (not found in the Colorista Free or in Rebel CC), if you want an advanced 3-way color corrector for AE and NLEs.
Recently in White Balance in Premiere Pro CC, instead of using the Fast Color Corrector, Eran Stern showed how to use the Cycore Color Neutralizer effect (included with After Effects) to white balance inside Premiere Pro. You have to do a little file management to enable the plug-in, and you need to use the older AECC version of the plug-in (not CC 2014), but it's useful for other CyCore effects too. CC Color Neutralizer was noted in Todd Kopriva's overview of AE CS6, by Lance Evans in Creative Bloq, and recently demonstrated in After Effects by Mikey Borup.
For After Effects, there are several options, most of which essentially move RGB balance or hue and saturation in the opposite direction of the color cast. Bob Currier explains how to auto white-balance using a feature of Synthetic Aperture Color Finesse that appeared in After Effects CS5:
The “Auto Color” button in Color Finesse (included with AE) will correct white-balance errors. The correction is based on the current frame, so choose an “average” frame to white balance to. To do white balance it's really simple: Apply Color Finesse to a layer. In the effect controls window, click the “Auto Color” button. You're done.
It may be apparent that Auto Color doesn't always work — don't be surprised if you have to dig deeper. See for example, Primary color correction in After Effects using Color Finesse and Secondary color correction in After Effects using Color Finesse by Andrew Devis:
Don't be scared away by the modal UI, there's a lot more to Color Finesse, so check out the Synthetic Aperture training resources page, which lists almost every resource available. There may be a few extra details on this effect, RGB Parade scopes, and other color correction resources in AE Help. If you're looking for tutorials on color, be sure to see Color correction and color grading tutorials, a 2011 motherload collection of color resources for AE and PPro by Todd Kopriva.
Adobe After Effects Professional Studio Techniques by Mark Chrsitiansen also covers correction, providing a solid basis for using Levels, Curves, Hue & saturation, and other fundamental image processing tools found in Photoshop, After Effects, and Premiere Pro. An excerpt of the CS3 edition can be found at the Adobe Press website. Mark says, “No skill is as essential for a compositor as the ability to take control of color authoritatively and conclusively, making foreground and background elements seem to inhabit the same world, ensuring that shots from a sequence are consistent with one another, and matching their overall look to the artistic direction of the project.”
Also, here's Steve Hullfish on Color Finesse from Color Correction In After Effects With Color Finesse — Day 1 (of 2):